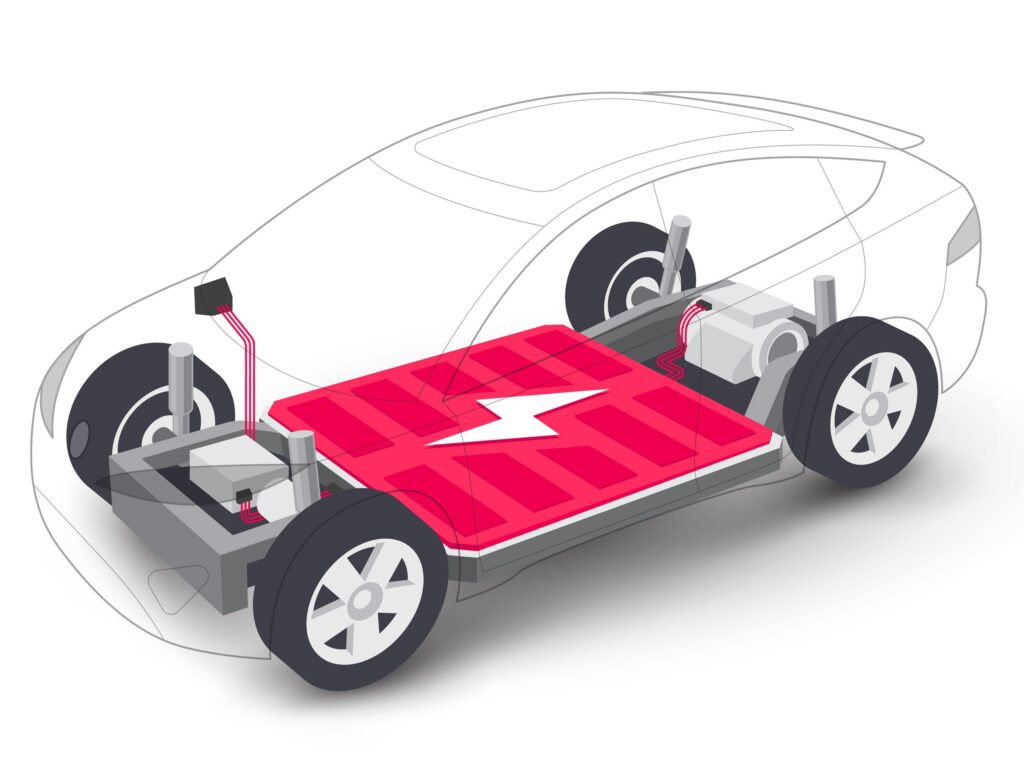
One of the most crucial parts of an electric vehicle is its batteries. Electric Vehicle Batteries are the lifeline. The primary source of energy powering an electric vehicle is electrical energy stored in its battery. The different types of electric car batteries rely on the vehicle’s system. Lithium-ion batteries are most frequently used in different electric vehicles. Batteries with zero emissions are designated as ZEBRA. NiMH batteries are the best option for hybrid electric vehicles. This article will provide a brief overview of the various electric vehicle battery types, their properties, and the battery management system (BMS) of an electric vehicle.

Types of Electric Vehicle Batteries
Batteries for electric vehicles differ from SLI batteries (starting, lighting, and ignition). SLI batteries are typically placed in cars that run on gasoline or diesel. This kind of electric car battery is made to be an energy storage device that can provide power for an extended, reliable, and long period of time.
This article will cover 5 different kinds of electric vehicle batteries:
- Lithium-Ion Battery (Li-On) – The Li-Ion battery is a type of electric car battery that is used most frequently in different electric vehicles. Most of us are already familiar with this type of battery as it is found in many electronic devices such as laptops and cell phones. The fundamental point which separates it from other types of batteries is that it is one of scale. This battery is superior to all others in terms of preserving its capacity and holds a full charge longer because it also has a low “self-discharge” level.
Also, Li-on batteries can be recycled, making them the ideal option for individuals who want to drive eco-friendly electric vehicles. This is the battery that is mostly used by PHEVs (Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles) and BEVs (Battery Electric Vehicles).
- Hybrid Nickel-Metal (NiMH) Batteries – Although some BEVs (Battery Electric Vehicles) have successfully used NiMH batteries, hybrid electric vehicles (HEV) use them more frequently. This particular hybrid electric vehicle battery does not rely on external power sources (can be recharged from an outside source of the car system). Batteries in hybrid electric vehicles recharge based on engine speed, wheel speed, and regenerative braking. Compared to SLA ( Lead Acids) or lithium-ion batteries, NiMH batteries have a longer lifespan. NiMH batteries are secure and can even withstand improper handling. The following are the main drawbacks of NiMH batteries:
- The cost is comparatively higher.
- High rate of self-discharge
- Produces a lot of heat at high temperatures.
3. Lead-Acid (SLA) Batteries – The earliest rechargeable batteries are SLA (lead-acid). Lead-acid batteries are heavier and lose capacity over time compared to lithium and NiMH batteries, but they are still reasonably inexpensive and safe. Large-capacity SLA electric vehicle batteries are currently being developed, but SLA batteries are currently only used as a secondary power storage system by commercial vehicles.
Some Other Battery Types
Ultra-Capacitor Batteries – The ultra-capacitor battery is actually not a battery in the usual sense. This kind of electric vehicle battery stores polarised liquid between the electrode and the electrolyte, in contrast to other electrochemical batteries. The liquid’s ability to store energy rises along with its surface area. Ultra-capacitor batteries are excellent choices for secondary power storage in electric vehicles, just like SLA batteries. Moreover, ultra-capacitors can give electric vehicles more power when accelerating using regenerative braking.
ZEBRA Batteries – The ZEBRA electric vehicle battery is a low-temperature sodium-sulfur (NaS) battery that was developed by ZEBRA, formerly known as (Zeolite Battery Research Africa) before changing its name to (Zero Emissions Batteries Research Activity) battery in 1985. In fact, ZEBRA batteries were created specifically for use in electric vehicle applications. The battery employs ceramic Na + beta-alumina electrolyte and NaAlCl4.
ZEBRA Electric Vehicle Batteries Characteristics
- These are high-power cells that can function as the battery for an electric vehicle.
- These high-temperature batteries can also function at temperatures above 270 °C.
- A nominal operating cell voltage of 2.58 Volts is provided by the chemical sodium nickel chloride (NaNiCl).
Battery Management System (BMS)
The purpose of a battery management system, also known as BMS, is to maximize the lifespan and other properties of an electric car battery. It is strongly advised that BMS be implemented in all battery-powered electric vehicles. The objective is to maintain the battery within the recommended functioning ranges. Any misuse such as overcharging, over discharging, or overheating can irreversibly harm lithium and NiMH battery chemicals. Installing a BMS will be extremely beneficial for all sorts of electric vehicle batteries.
Unique Features of BMS
The battery management system has some unique features, such as:
- Charge balancing, which makes sure that all cells are fully charged at the same time and guards against overcharging-related damage.
- Active balancing, which involves moving energy from stronger to weaker cells to make sure that all cells reach the maximum discharge point simultaneously.
- Temperature monitoring is necessary to prevent harm from overheating.
- Low-voltage cut-off is a technique to isolate a battery and prevent misuse damage when any cell reaches the advised minimum voltage.
- Monitoring of all battery cells’ Status of Charge (SOC) for electric vehicles. The capacity of each cell can be determined by monitoring voltage and current.
Conclusion
So, these are the types of batteries that are used in Electric Vehicles. We have discussed different types of batteries, their function, and their management system to make their life longer.